Oct 20, 2018 原创文章
Hello Pytorch 壹 -- 卷积层原理及实现
代码:https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/_modules/torch/nn/modules/conv.html
官方文档:https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html#convolution-layers
动画演示:https://github.com/vdumoulin/conv_arithmetic
卷积与互相关计算
在深度学习领域,卷积定义为图像矩阵和卷积核的按位点乘,实质这种操作是互相关运算,而卷积需要把卷积核顺时针旋转180度然后再做点乘。
参见:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cross-correlation
在信号处理领域,互相关计算可以用来计算两个信号之间的相似性,也通过与已知信号比较用于寻找未知信号中的特性。
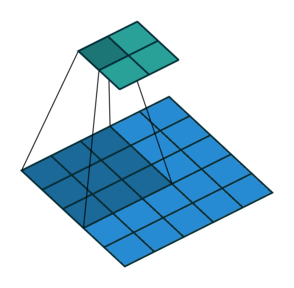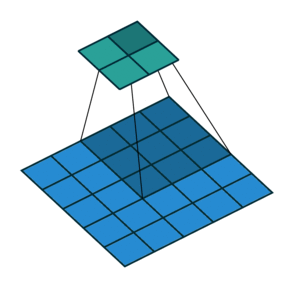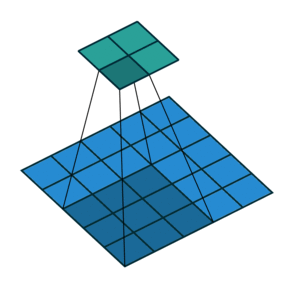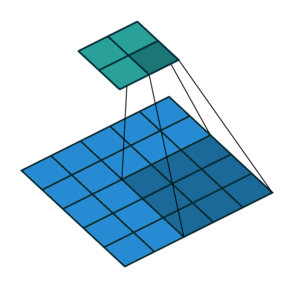
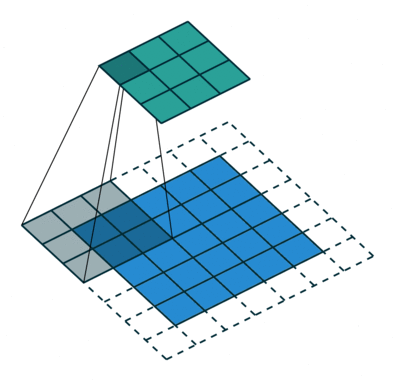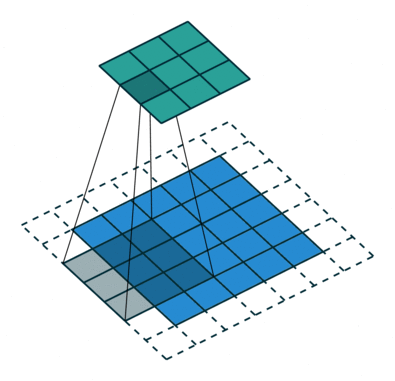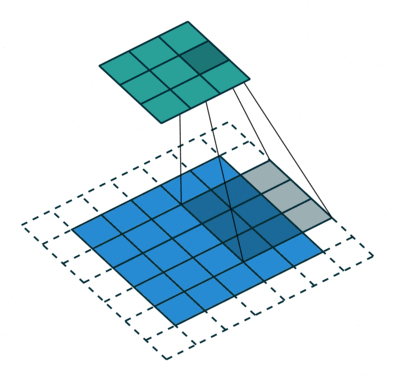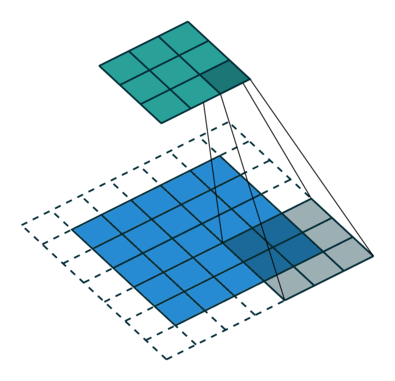
卷积
动画演示
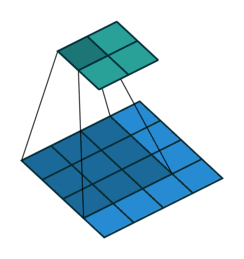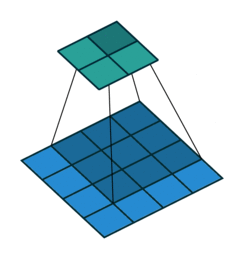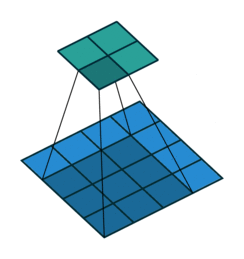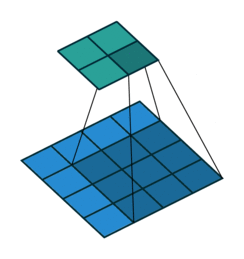 |
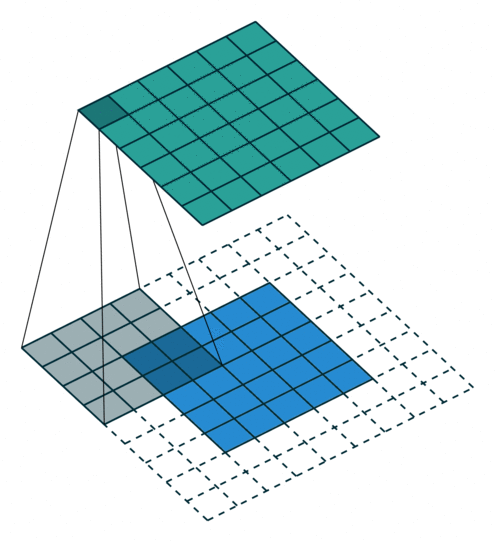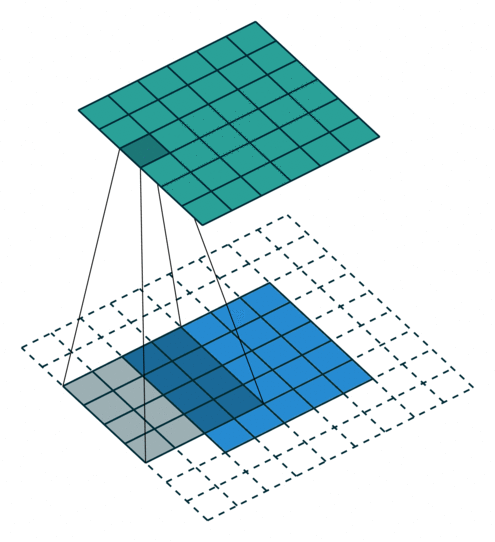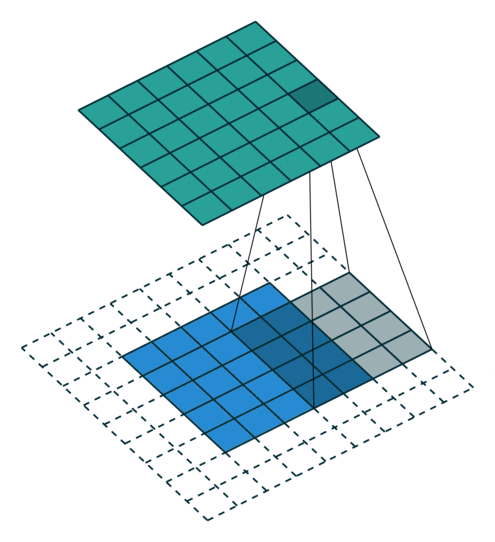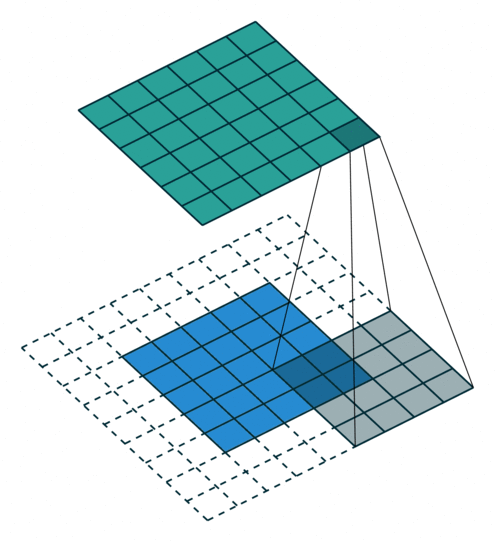 |
| No padding, no strides | Arbitrary padding, no strides |
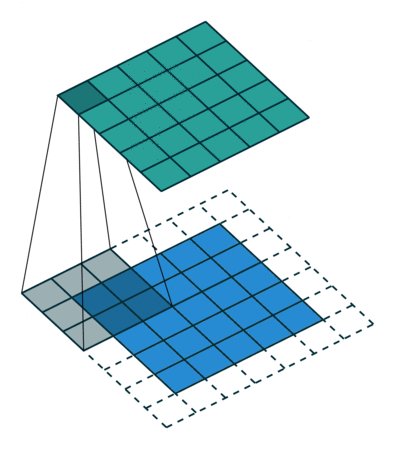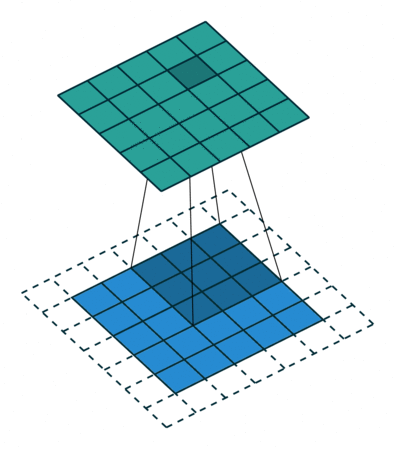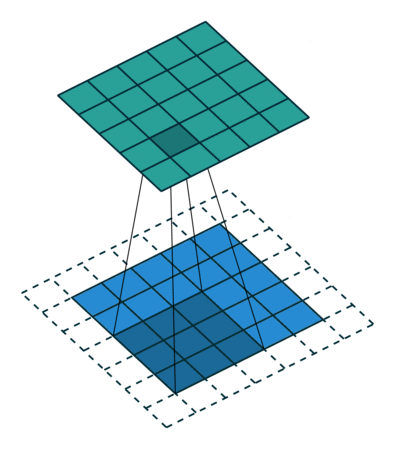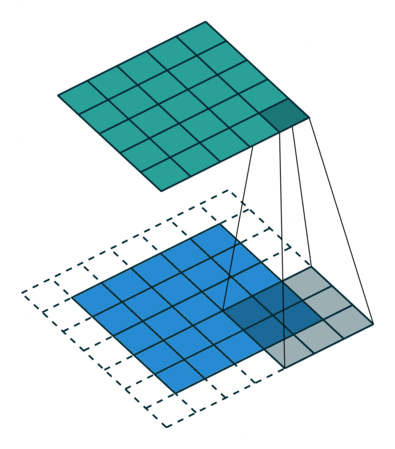 |
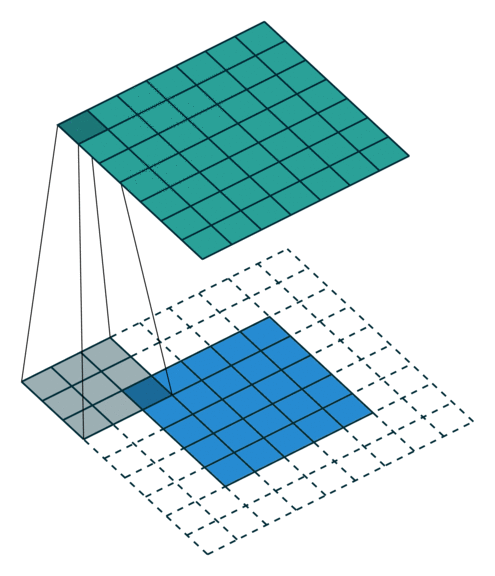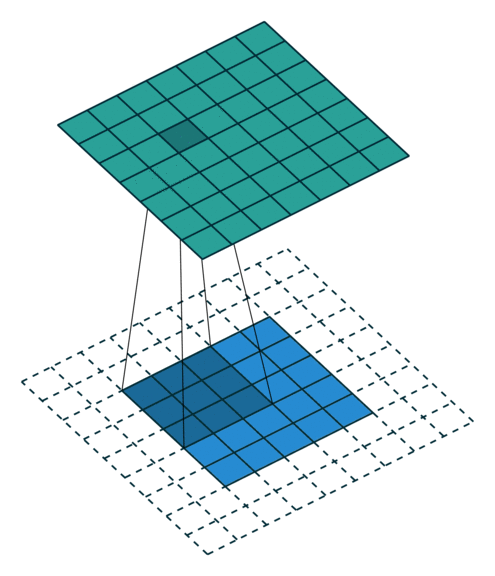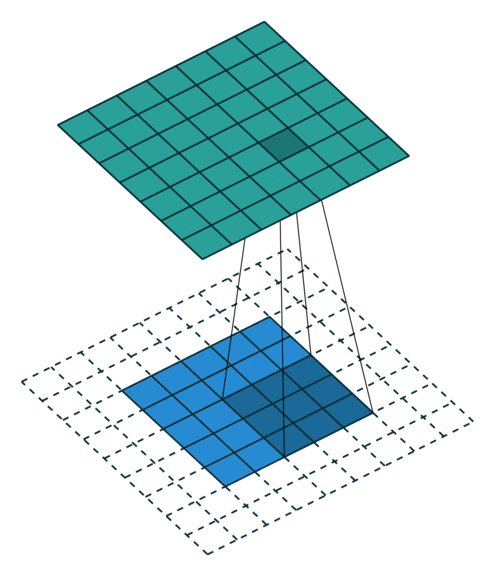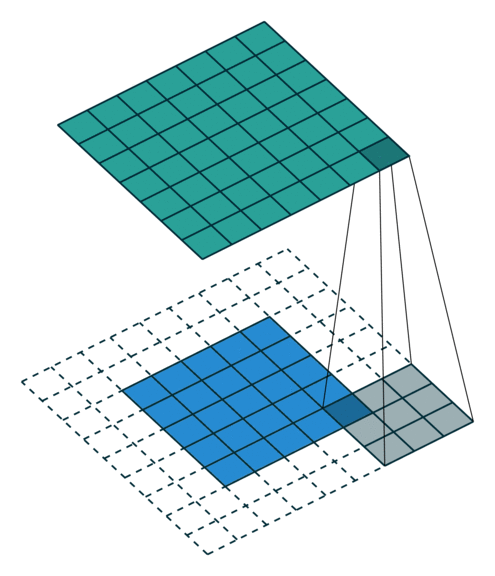 |
| Half padding, no strides | Full padding, no strides |
 |
 |
| No padding, strides | Padding, strides |
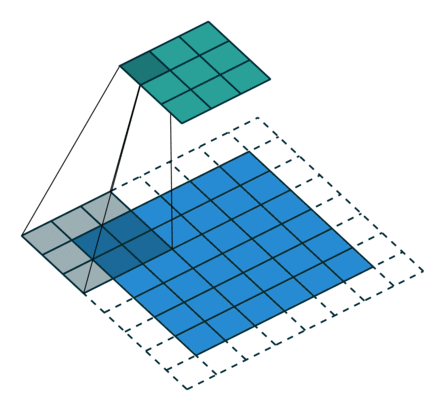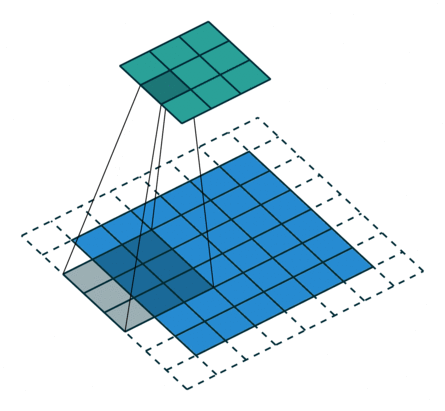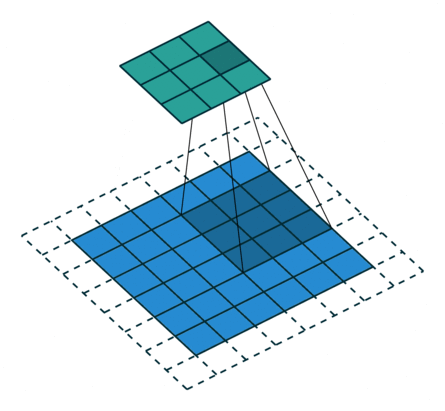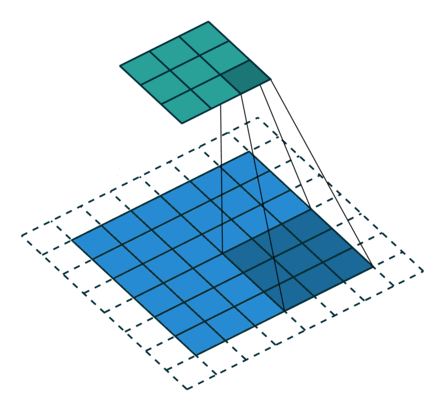 |
|
| Padding, strides (odd) |
N.B.: Blue maps are inputs, and cyan maps are outputs.
二维卷积 torch.nn.Conv2d
class torch.nn.Conv2d (in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True)
输入数据大小:$(N, C_{in}, H, W)$
输出数据大小:$(N, C_{out}, H_{out}, W_{out})$
2D 卷积的整个过程以下式表达:
其中 $\star$ 是 2D 互相关操作符, N 表示批(batch)的大小, C 表示通道数, H 输入数据的高(像素), and W 表示数据的宽(像素)
其他参数
kernel_size (int or tuple) : 控制卷积核的大小。
stride (int or tuple, optional) : 控制互相关的步长。
padding (int or tuple, optional) : 控制两侧隐式零填充的数量,以填充每个维度的点数。
dilation (int or tuple, optional) : 控制卷积核核点之间的间距。具体操作过程如下图所示,可以很好地显示扩张的作用

groups (int, optional) : 控制输入和输出的连接。输入数据和输出数据的通道数必须同时被groups整除。例如:groups=1时,所有的输入卷积到所有的输出。groups=2时,有两个并列的卷积层,每个卷积层对应输入数据一半的通道数,同时也对应输出数据一半的通道数。groups= in_channels (输入数据的通道数)时 每个输入通道与对应的大小为 $\left\lfloor\frac{\text{out_channels}}{\text{in_channels}}\right\rfloor$ 的滤波器集合做卷积运算 。
深度卷积:当 groups == in_channels,out_channels == K * in_channels (其中K为正整数)时,被称为深度卷积。
输入数据大小:$(N, C_{in}, H_{in}, W_{in})$
输出数据大小:$(N, C_{out}, H_{out}, W_{out})$
其中:
一维卷积 torch.nn.Conv1d
class torch.nn.Conv1d (in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True)
输入数据大小:$(N, C_{in}, L)$
输出数据大小: $(N, C_{out}, L_{out})$
1D 卷积的整个过程以下式表达:
其中 $\star$ 是 1D 互相关操作符, N 表示批(batch)的大小, C 表示通道数, L表示一维数据的长度。
多通道一维数据:
一维卷积常用于序列模型,自然语言处理领域。以声音为例,在同一维度上,不同的通道可以表示不同的音源的声音,通道1:人声,通道2:鼓声。即:不同的通道表示不同属性的一维序列数据。
关于一维卷积其余的属性和算法和下文中的二维卷积相似。
三维卷积 torch.nn.Conv3d
class torch.nn.Conv3d (in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True)
相比于二维卷积,三维卷积的输入和输出是三维数据。输入数据的大小为:$(N, C_{in}, D, H, W)$,输出数据的大小为:$(N, C_{out}, D_{out}, H_{out}, W_{out})$
其余的概念和算法与二维卷积相同。
三维卷积的应用场景: 三维卷积常用于医学领域(CT影响),视频处理领域(检测动作及人物行为)
反卷积(转置卷积)
卷积操作的作用类似神经网络中的编码器,用于对高维数据进行低维特征提取,而 反卷积 通常用于将低维特征映射成高维输入,与卷积操作的作用相反。同时也是一种基于学习的上采样实现方法。
动画演示
 |
 |
| No padding, no strides, transposed | Arbitrary padding, no strides, transposed |
 |
 |
| Half padding, no strides, transposed | Full padding, no strides, transposed |
 |
 |
| No padding, strides, transposed | Padding, strides, transposed |
 |
|
| Padding, strides, transposed (odd) |
N.B.: Blue maps are inputs, and cyan maps are outputs.
二维反卷积 torch.nn.ConvTranspose2d
class torch.nn.ConvTranspose2d (in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, output_padding=0, groups=1, bias=True, dilation=1)
反卷积和卷积在参数上的区别在于padding和output_padding。
padding :控制0填充的大小。在输入数据的每个边隐式地添加 (kernel_size - 1 - padding) 个0。而在进行卷积操作时,需要填充的是(padding)个0。
output_padding Additional size added to one side of each dimension in the output shape
The padding argument effectively adds kernel_size - 1 - padding amount of zero padding to both sizes of the input. This is set so that when a Conv3d and a ConvTranspose3d are initialized with same parameters, they are inverses of each other in regard to the input and output shapes. However, when stride > 1, Conv3d maps multiple input shapes to the same output shape. output_padding is provided to resolve this ambiguity by effectively increasing the calculated output shape on one side. Note that output_padding is only used to find output shape, but does not actually add zero-padding to output.
输入数据大小:$(N, C_{in}, H_{in}, W_{in})$
输出数据大小:$(N, C_{out}, H_{out}, W_{out})$
其中:
一维反卷积 torch.nn.ConvTranspose1d
class torch.nn.ConvTranspose1d (in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, output_padding=0, groups=1, bias=True, dilation=1)
在计算方法和参数设置上与二维反卷积相似。
三维反卷积 torch.nn.ConvTranspose3d
class torch.nn.ConvTranspose3d (in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, output_padding=0, groups=1, bias=True, dilation=1)
在计算方法和参数设置上与二维反卷积相似。
相关文章:
初识VGG网络模型 # VGG, 卷积网络, 卷积层, 论文阅读 Dec 24, 2018 原创文章Hello Pytorch 肆 -- 激活函数 # 深度学习, Pytorch, 激活函数 Nov 02, 2018 原创文章
Hello Pytorch 叁 -- 简单理解生成对抗网络(GAN) # 深度学习, Pytorch, 生成对抗网络, GAN Oct 29, 2018 原创文章
Hello Pytorch 贰 -- 常用损失函数 # 深度学习, Pytorch, 损失函数, 交叉熵 Oct 20, 2018 原创文章
Hello Pytorch 零 -- 搭建年轻人的第一个神经网络:LeNet # 深度学习, Pytorch, LeNet, CIFAR-10, CNN Oct 19, 2018 原创文章



